Diaper rash is a very common condition that can cause a baby's skin to become sore, red and tender. Irritant diaper dermatitis, also known as "diaper dermatitis" or "napkin dermatitis“ and commonly known as diaper rash or nappy rash, is a generic term applied to skin rashes in the diaper area that are caused by various skin disorders and/or irritants.
It is noticed in other parts of a baby's body, too, as a common form of inflamed skin (dermatitis) that appears as a patchwork of bright red skin on the baby's bottom. Diaper rash can alarm parents and annoy babies.
Diaper rash is the most common dermatitis found in infancy. Prevalence has been variably reported from 4-35% in the first 2 years of life. Incidence triples in babies with diarrhea. It is not unusual for every child to have at least 1 episode of diaper rash by the time he or she is toilet-trained.
Because fewer than 10% of all diaper rashes are reported by the family, the actual incidence of this condition is likely underestimated.
The incidence is lower among breastfed infants—perhaps due to the less acidic nature of their urine and stool. Babies wearing superabsorbent disposable diapers with a central gelling material have fewer episodes of diaper dermatitis compared with their counterparts wearing cloth diapers.

The precise etiology of most diaper rashes is not clearly defined. They likely result from a combination of factors that includes wetness, friction, urine and feces, and the presence of microorganisms. Anatomically, this skin region features numerous folds and creases, which present a problem with regard to both efficient cleansing and control of the microenvironment.
The main irritants in this situation are fecal proteases and lipases, whose activity is increased greatly by elevated pH. An acidic skin surface is also essential for the maintenance of the normal microflora, which provides innate antimicrobial protection against invasion by pathogenic bacteria and yeasts. Fecal lipase and protease activity is also greatly increased by acceleration of gastrointestinal transit; this is the reason for the high incidence of irritant diaper dermatitis observed in babies who have had diarrhea in the previous 48 hours.
The wearing of diapers causes a significant increase in skin wetness and pH. Prolonged wetness leads to maceration (softening) of the stratum corneum, the outer, protective layer of the skin, which is associated with extensive disruption of intercellular lipid lamellae. A series of diaper studies conducted mainly in the late 1980s found a significant decrease in skin hydration following the introduction of diapers with a superabsorbent core. Recent studies confirm that this trend is ongoing. Weakening of its physical integrity makes the stratum corneum more susceptible to damage by (1) friction from the surface of the diaper and (2) local irritants.
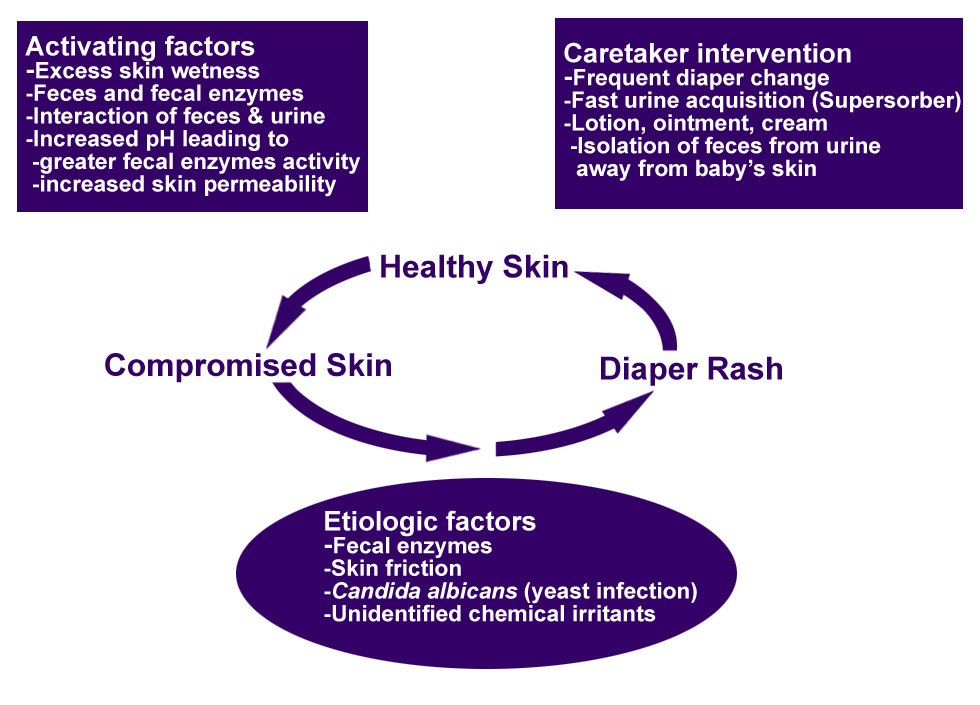
The normal pH of the skin is between 4.5 and 5.5. When urea from the urine and stool mix, urease breaks down the urine, decreasing the hydrogen ion concentration (increasing pH). Elevated pH levels increase the hydration of the skin and make the skin more permeable.

Identifying a diaper rash is usually easy. The rash is located on skin underneath the diaper area. Sometimes the rash might go up onto the baby’s tummy and bottom. Some areas of skin might be raised or swollen, and there might be some ulcers. Diaper rash is characterized by the following:
Skin signs - Diaper rash is marked by red, puffy and tender-looking skin in the diaper region — buttocks, thighs and genitals. It may appear all over baby's bottom or genital area, or only in certain places.
Changes in baby's disposition - It is noticed that baby seems more uncomfortable than usual, especially during diaper changes. A baby with a diaper rash often fusses or cries when the diaper area is washed or touched.


-
Traditional Cream
-
per - Yes
- Difficult
- Poor barriers
- Yes
- Yes
- Yes
-
Almond Baby Skin Care
-
per - No
- Simple (glides very smoothly)
- Thicker barriers Combination of 5 ingredients
- No
- No
- No

